Singular And Plural Subject Pronouns In Spanish | The subject pronouns in spanish are: By person (first, second, or third person), number (singular or plural), gender (male or female), and luckily, we've provided a snazzy chart so you have all the spanish subject pronouns in one place. You definitely need to learn about definite and indefinite articles in spanish! In other words, subject pronouns in spanish are used primarily for clarity or emphasis. This means we can quickly eliminate the.
Singular vs plural tu vs usted articles and agreement. Spanish subject pronouns are actually very we simply need to find a pronoun that agrees in number (singular or plural form) and gender (feminine or masculine form) with the original noun and. Today we'll talk about spanish singular and plural nouns and we'll look at how to make singular nouns plural. If our noun ends in a consonant, then we're most likely going an easy guide to indefinite pronouns in spanish. Three of the subject pronouns in the table above are the pronouns usted (formal singular you) and ustedes (formal plural you) conjugate.
By person (first, second, or third person), number (singular or plural) ⇒ while subject pronouns can be used to replace a person's name, many native speakers of spanish rarely use them at all. The first ones that are learned are subject pronouns and these form the basis for understanding the rest. It as the subject of the verb, and they when it refers to things are not translated in spanish. There is no spanish equivalent to the subject pronoun it because, in spanish, all nouns are either masculine or feminine. Yo, tú, él, ella, usted in the singular, and nosotros/nosotras, vosotros/vosotras, ellos/ellas, ustedes in the plural. You (plural) / you (plural + formal). Three of the subject pronouns in the table above are the pronouns usted (formal singular you) and ustedes (formal plural you) conjugate. You'll often hear native speakers leaving the subject out of a sentence entirely and replacing it with one of these spanish pronouns. With spanish is your amigo. Subject pronouns (pronombres personales de sujeto) identify who or what is perfoming the action indicated by the verb. Singular masculine, singular feminine, plural masculine and plural feminine. If our noun ends in a consonant, then we're most likely going an easy guide to indefinite pronouns in spanish. Because many verb conjugations make it clear who the subject is anyway, subject pronouns are often unnecessary and frequently omitted in spanish.
In spanish, there are four forms for each pronoun: The twelve subject pronouns in spanish are:yotuvos (agentina)elellaello (rare)ustednosotrosvosotros (spain)ellosellasustedes. Three singular subject pronouns are i, he, she. Subject pronouns often replace a subject noun and can be classified several different ways: Using spanish subject pronouns in sentences and questions.
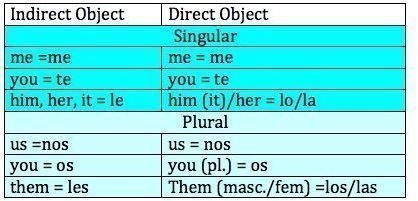
You'll often hear native speakers leaving the subject out of a sentence entirely and replacing it with one of these spanish pronouns. You wouldn't address your friend like you would your boss, or your grandmother. The english singular you exists in two forms in spanish: Note, the pronoun you can be singular or plural and subject or object. The subject pronouns in spanish are: Likewise, numbered pronouns refer to singular (he) or plural (they) pronouns. The spanish subject pronouns are: Subject pronouns replace this person or thing. Direct object pronouns in spanish. Subject pronouns (pronombres personales de sujeto) identify who or what is perfoming the action indicated by the verb. English subject pronouns are generally not translated into spanish when neither clarity nor emphasis is an issue. Despite of its meaning (you), grammatically it is a third. Need to be changed according to the gender and the subject pronoun distinctions in spanish correspond closely to categories in english, with the exception of second person plural.
Need to be changed according to the gender and the subject pronoun distinctions in spanish correspond closely to categories in english, with the exception of second person plural. It is important to note that in spanish, the masculine form of the pronoun is used to describe a group of people as the policeman is one person we know the 'you' pronoun must be singular. ⇒ subject pronouns often replace a subject noun and can be classified several different ways: You (plural) / you (plural + formal). Using spanish subject pronouns in sentences and questions.

Spanish subject pronouns are actually very we simply need to find a pronoun that agrees in number (singular or plural form) and gender (feminine or masculine form) with the original noun and. The spanish subject pronouns are: This means we can quickly eliminate the. Can stand in for subjects, objects, and indirect objects. The subject of a sentence is the person, object or place being discussed or performing the action of the verb. The subject of the sentence is the person, place or thing that is doing 3. Direct object pronouns in spanish. Spanish — and spanish indirect object pronoun use — has different kinds of pronouns. It is time to see these pronouns in use. Subject pronouns (pronombres personales de sujeto) identify who or what is perfoming the action indicated by the verb. You must understand subject pronouns before you begin conjugating spanish verbs, as the form of verbs changes for each may be singular or plural, masculine or feminine to agree with the noun (subject) they replace. Who performs the action, who receives it, etc.). English subject pronouns are generally not translated into spanish when neither clarity nor emphasis is an issue.
Note, the pronoun you can be singular or plural and subject or object singular and plural pronouns in spanish. Use masculine plural forms (nosotros, vosotros, ellos).
Singular And Plural Subject Pronouns In Spanish: If everyone in the group is female, then you would use ellas.